Blog
The TOPBEST Library of Blogs is a valuable resource for visitors. Our objective is to provide knowledge about pests and ways to create a safe and pest-free environment.Ka-trabaho ko, mga Everyday Heroes
Kailangan ba may kapa para maging Hero? Ang kailangan handa sa laban. Naka-full safety gear ang mga technicians. Ang panlaban…
Ang Swarming ay Warning!
Sa unang tingin, dramatic, parang sine. Maliliit sila, grupo-grupo kung lumipad sa ere. Minsan pumapaligid sa ilaw. Sa nakaka-alam, matinding…
4 Common Ant Species in the Philippines
What are the common ant species in the Philippines? Anywhere you may be in the world, the chances are high…
Who Bit Me? Identifying Bug Bites
Bug bites can vary from unnoticed, to annoying, to potentially dangerous. Sometimes you won’t even notice you’ve been bitten until…
Mga Natural at Mabisang Pamatay sa Anay
Ano ang mga natural at mabisang pamatay sa anay? Ang mga anay ay mga pesteng pwedeng sumira ng iyong tahanan—lalo na kung…
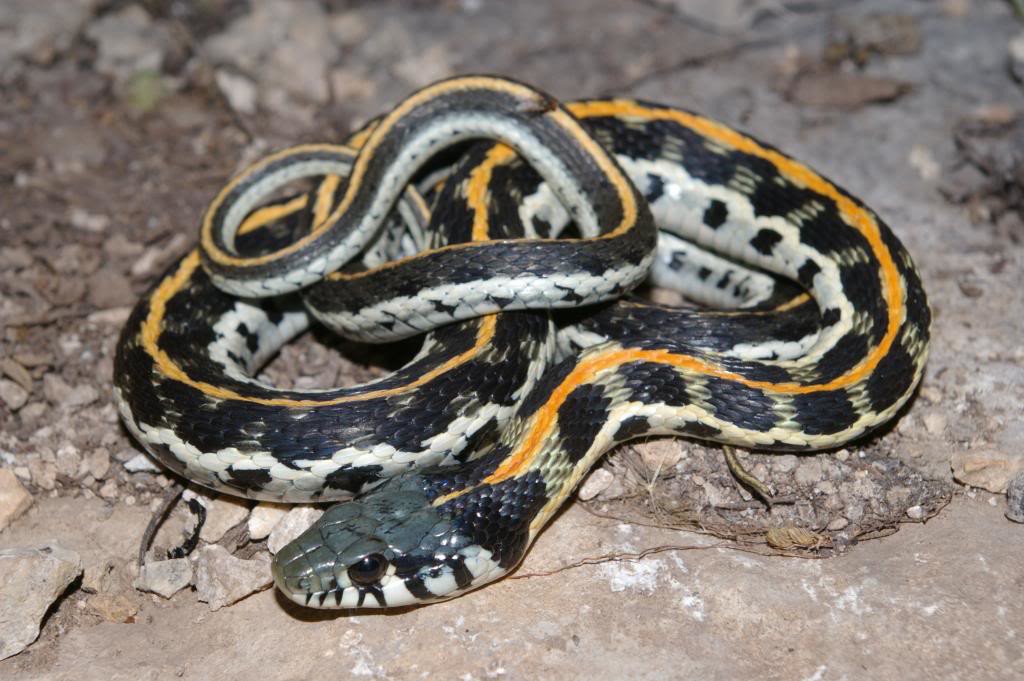
Come Hither and Slither: 7 Non-Deadly Snakes You Can Keep as Pets
Though not as common as cockroaches, rats, and other critters, snakes are still among the top vermin faced by pest…
How to Insect-Proof Your Video Game Console
How can you insect-proof your video game console? Keeping your home free from pests is the main goal for getting…
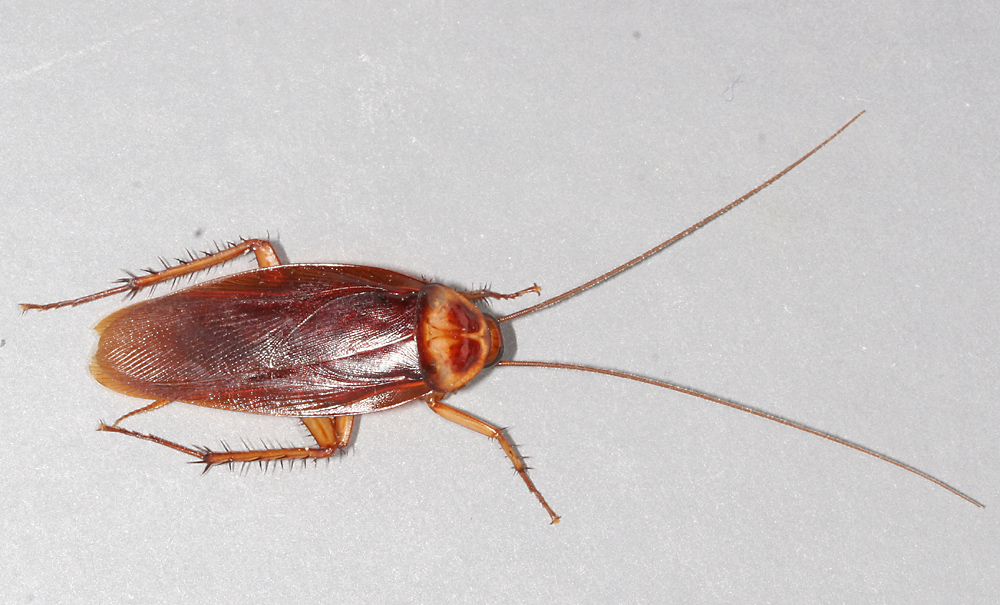
4 Most Commonly Found Cockroaches in the Philippines
What are the most commonly found cockroaches in the Philippines? If you live in the Philippines, then you’re no stranger…
How to Treat a Cockroach Bite at Home
What are the ways to treat a cockroach bite? Cockroach bites are common in the Philippines. If you find them…
3 Common Mosquito Species in the Philippines
What are the common mosquito species in the Philippines? Anyone who lives in the Philippines would be aware that mosquitoes…
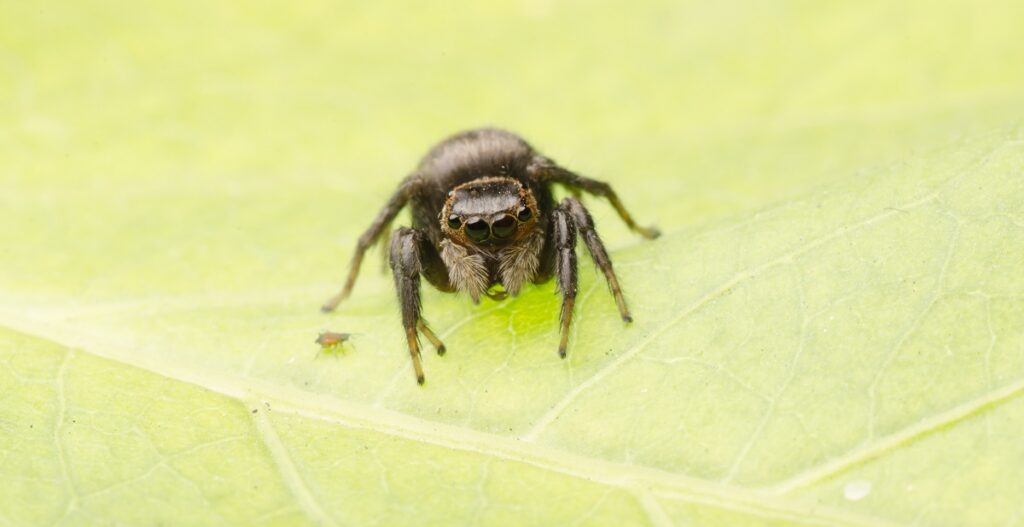
5 Common Types of Spiders in the Philippines
What are the common types of spiders in the Philippines? Huntsman Spider If you live in the Philippines, then you…
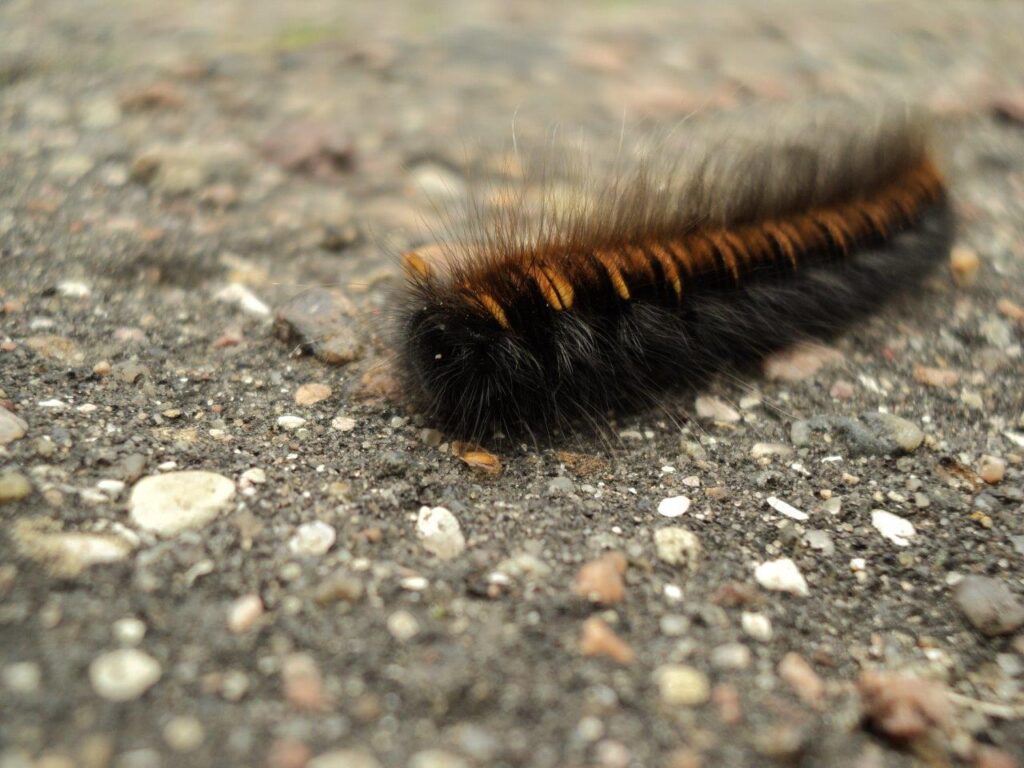
How to Treat a Hairy Caterpillar Rash
What are the ways to treat a hairy caterpillar rash? Most of us have probably experienced the sting which comes…